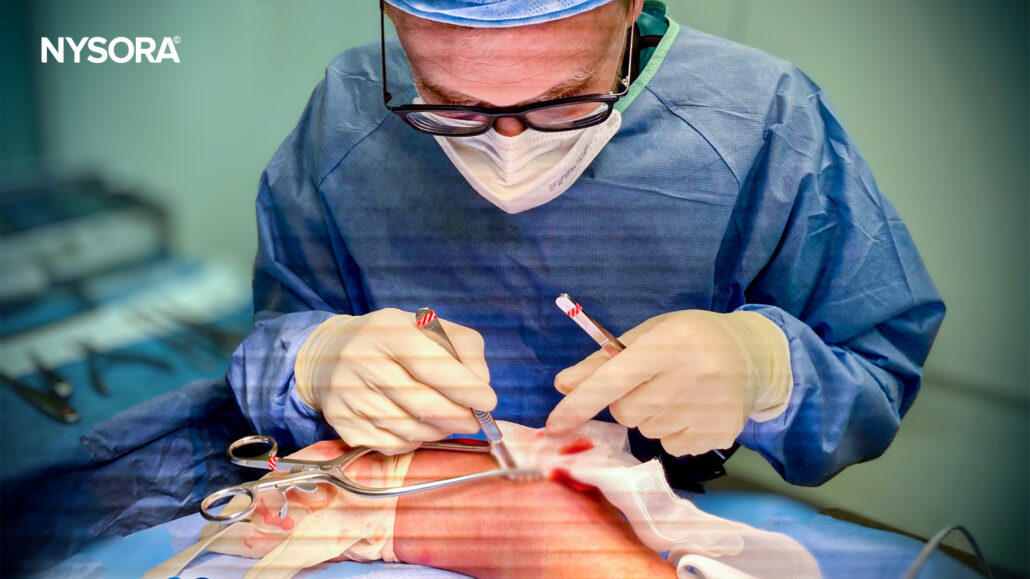
Case Study: Calcaneus fracture
The calcaneus, or the heel bone, is the most commonly fractured tarsal bone and accounts for about 1-2% of all fractures and ~60% of tarsal fractures. Calcaneal fractures most commonly occur during high-energy events leading to axial loading of the bone but can occur with any injury to the foot and ankle. Here’s what you need to know about the blocks we used to repair the fracture.
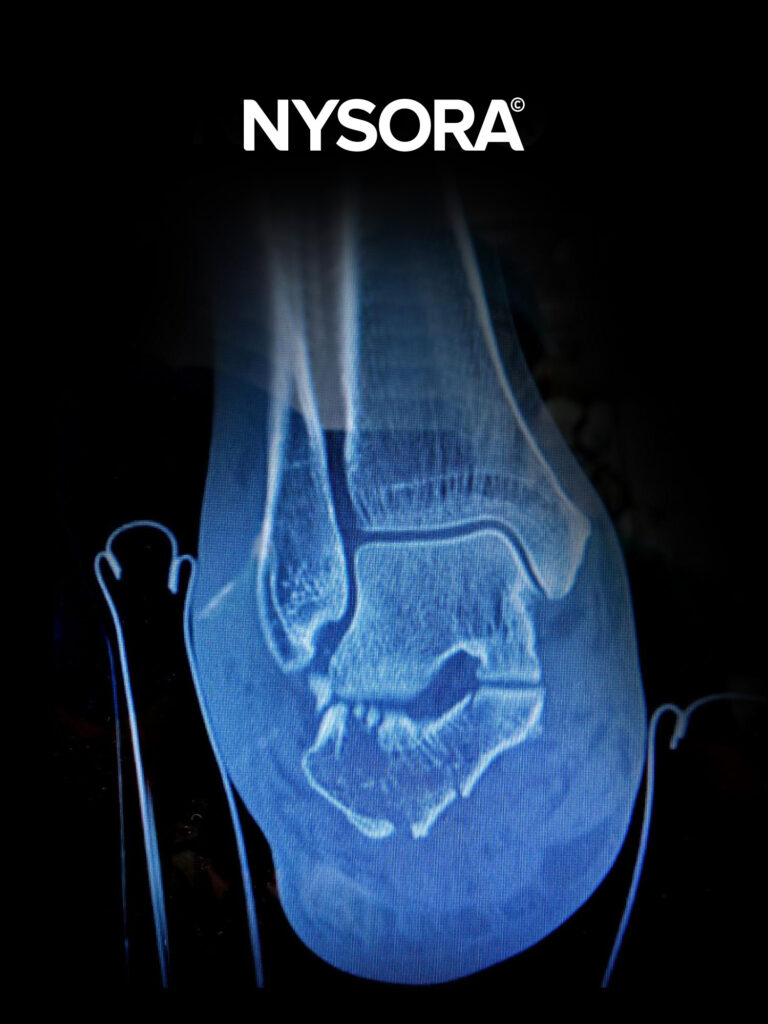
The calcaneus fracture repair was performed under a popliteal and adductor canal block.
- Popliteal block: One injection of 15 mL of 1% ropivacaine into the sciatic nerve sheath in the popliteal fossa.
Adductor canal block: 5 mL of 1% ropivacaine for tourniquet pain. The tourniquet is positioned just below the knee.
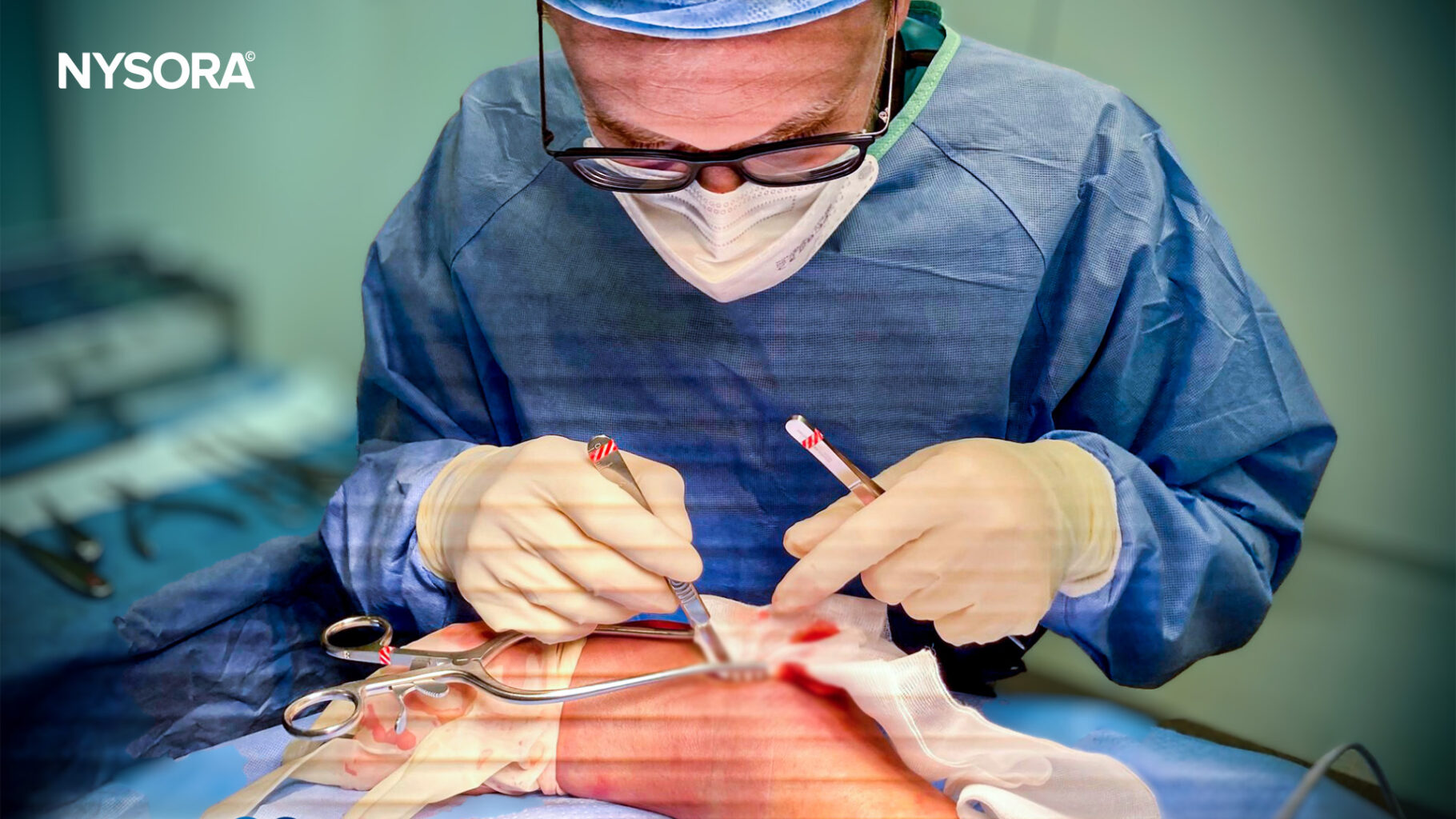
The combination of the two blocks serves as a complete anesthetic and postoperative analgesia in these patients.
For more case studies like these and the complete guide to the 60 most frequently used nerve blocks, download the Nerve Blocks App HERE. Don’t miss the chance to get the bestselling NYSORA Nerve Blocks App also in book format – the perfect study companion with the Nerve Blocks app!



