Learning objectives
- Describe the mechanisms of aneurysms and hemorrhage
- Describe the risk factors for aneurysms
- Recognize and treat aneurysmal hemorrhage
- Manage patients undergoing endovascular coiling
Definition & mechanisms
- Stroke is the second leading cause of death and the third most common cause of disability worldwide
- Hemorrhagic strokes account for about 32% of all strokes globally and can be caused by subarachnoid hemorrhage or intracerebral hemorrhage
- Most spontaneous (nontraumatic) subarachnoid hemorrhages are caused by ruptured saccular aneurysms
- Intracranial aneurysms are estimated to occur with a prevalence of 3.2% in the general population
- Aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage accounts for approximately 5% of strokes and is caused by the rupture of an intracranial aneurysm, an acquired focal abnormal dilation of an arterial wall
Aneurysm risk factors
- Smoking
- Hypertension
- Connective tissue disorders
- Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease
- Ehlers–Danlos syndrome type IV
- Neurofibromatosis type 1
- Marfan syndrome
- Coarctation of the aorta
- Genetic predisposition
Hemorrhage: Signs & symptoms
- Sudden onset of “worst headache of life”
- Loss of consciousness
- Nausea and/or vomiting
- Nuchal rigidity
- Photophobia
- Seizure
Hemorrhage treatment
- Immediate management: Directed at stabilizing life-threatening conditions, minimizing neurologic injury, optimizing physiology and planning definitive care
- Ensure a patent airway and adequate oxygenation and ventilation
- External ventricular drain
- Control acute hypertension
- Control of headache with analgesics, anxiolysis, and bed rest
- Stop and reverse anticoagulant therapy
- Administer nimodipine (60mg orally or by nasogastric tube every 4h, starting within 48h of hemorrhage and continued for 21 days)
- Definitive care
- Surgical clipping or endovascular coiling
Endovascular coiling: Anesthetic management
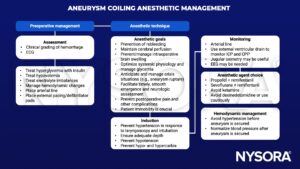
ICP, intracranial pressure; CPP, cerebral perfusion pressure
Keep in mind
- The optimal anesthetic technique depends on patient characteristics, severity of the aneurysm, and monitoring
Suggested reading
- Deepak Sharma; Perioperative Management of Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: A Narrative Review. Anesthesiology 2020; 133:1283–1305
- Campos JK, Lien BV, Wang AS, Lin LM. Advances in endovascular aneurysm management: coiling and adjunctive devices. Stroke Vasc Neurol. 2020;5(1):14-21. Published 2020 Mar 15.
- Abd-Elsayed AA, Wehby AS, Farag E. Anesthetic management of patients with intracranial aneurysms. Ochsner J. 2014;14(3):418-425.
We would love to hear from you. If you should detect any errors, email us customerservice@nysora.com