Learning objectives
- Anesthetic management of a patient with diabetes mellitus type 2
- Physiological changes due to diabetes mellitus
Definition and mechanisms
- Diabetes mellitus type 2 is a consequence of peripheral resistance to insulin action
- Is characterized by insulin resistance (hepatic, extrahepatic, or both) probably due to a decreased stimulation of glycogen synthesis in muscle by insulin, related to impaired glucose transport
- Insulin secretion and/or insulin action are thought to be deficient with excessive hepatic glucose production
- It is frequently associated with dysfunction in pancreatic β-cells responsible for insulin secretion
- The age of onset is variable, however, it is usually a disease of adults with slow onset
- Ketoacidosis is uncommon
Physiological changes
| Musculoskeletal system | Stiff joint syndrome (SJS) |
|---|---|
| Renal | Diabetic nephropathy |
| Neurological system | Increased risk of cerebrovascular accident (CVA) Nerve fibers at risk for ischemic injury Peripheral neuropathies |
| Autonomic neuropathy | Diabetic autonomic neuropathy Resting tachycardia Orthostatic hypotension Intestinal constipation Gastroparesis Bladder dysfunction Impaired neurovascular function Loss of autonomic response to Hypoglycemia |
| Cardiovascular system | Hypertension Coronary artery disease Silent myocardial ischemia Systolic and diastolic heart failure Congestive heart failure Peripheral vascular disease |
| Retinal | Diabetic retinopathy |
Management of diabetes mellitus type 2
- Diet
- Exercise
- Medications:
- Sulphonylureas (e.g. gliclazide)
- Biguanides (e.g. metformin)
- Thiazolidinediones (e.g. pioglitazone, rosiglitazone)
- Meglinitides (e.g. repaglinidine, nateglinide)
- Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors (e.g. acarbose, miglitol)
- Incretin mimetics:
- GLP-1 agonists (e.g. exanatide, liraglutide)
- DPP-4 inhibitors (e.g. sitagliptin and vildagliptin)
- SGLT2 inhibitors (e.g. canagliflozin, dapagliflozin, empagliflozin)
Anesthetic management
Preoperative assessment

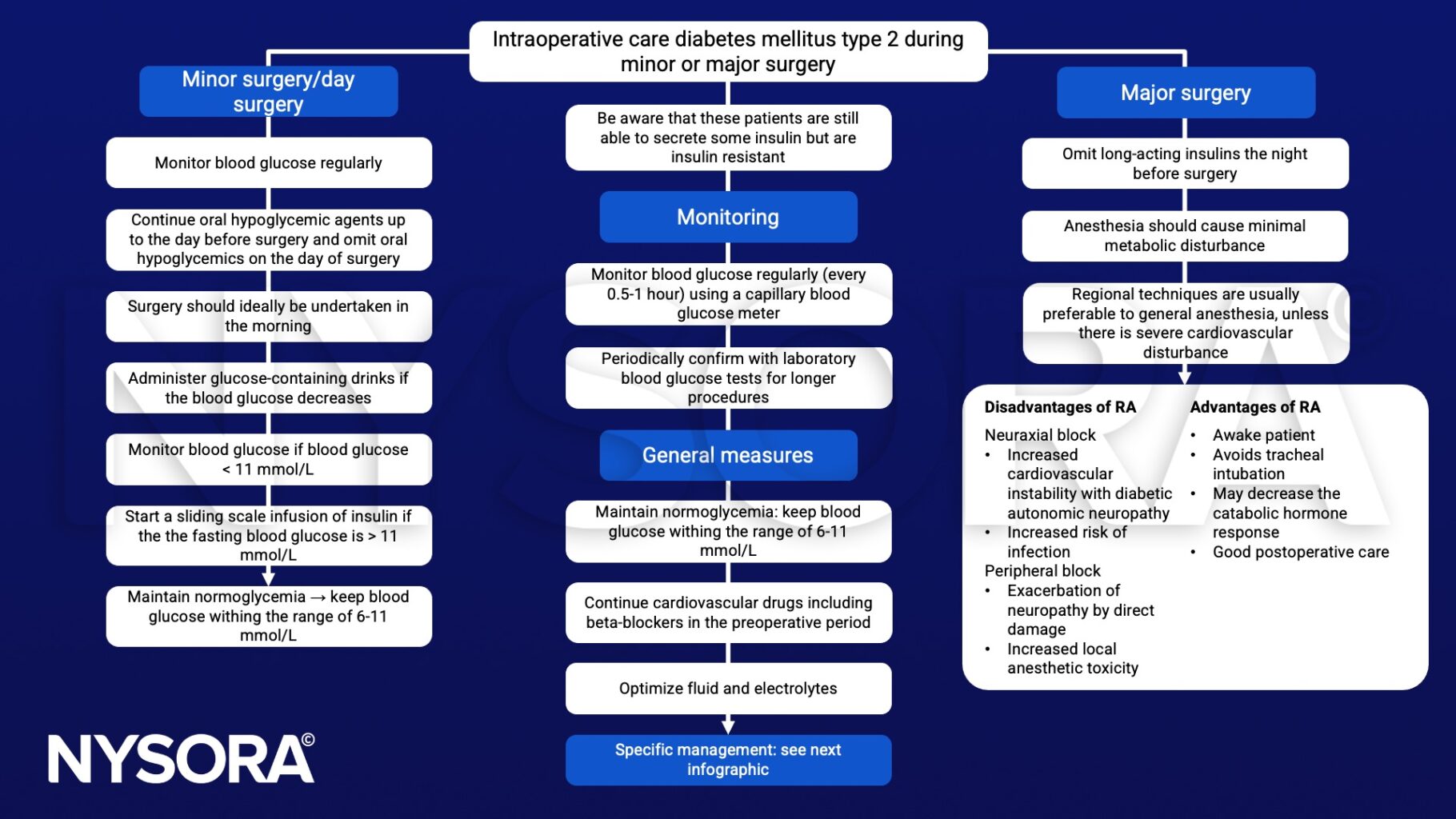
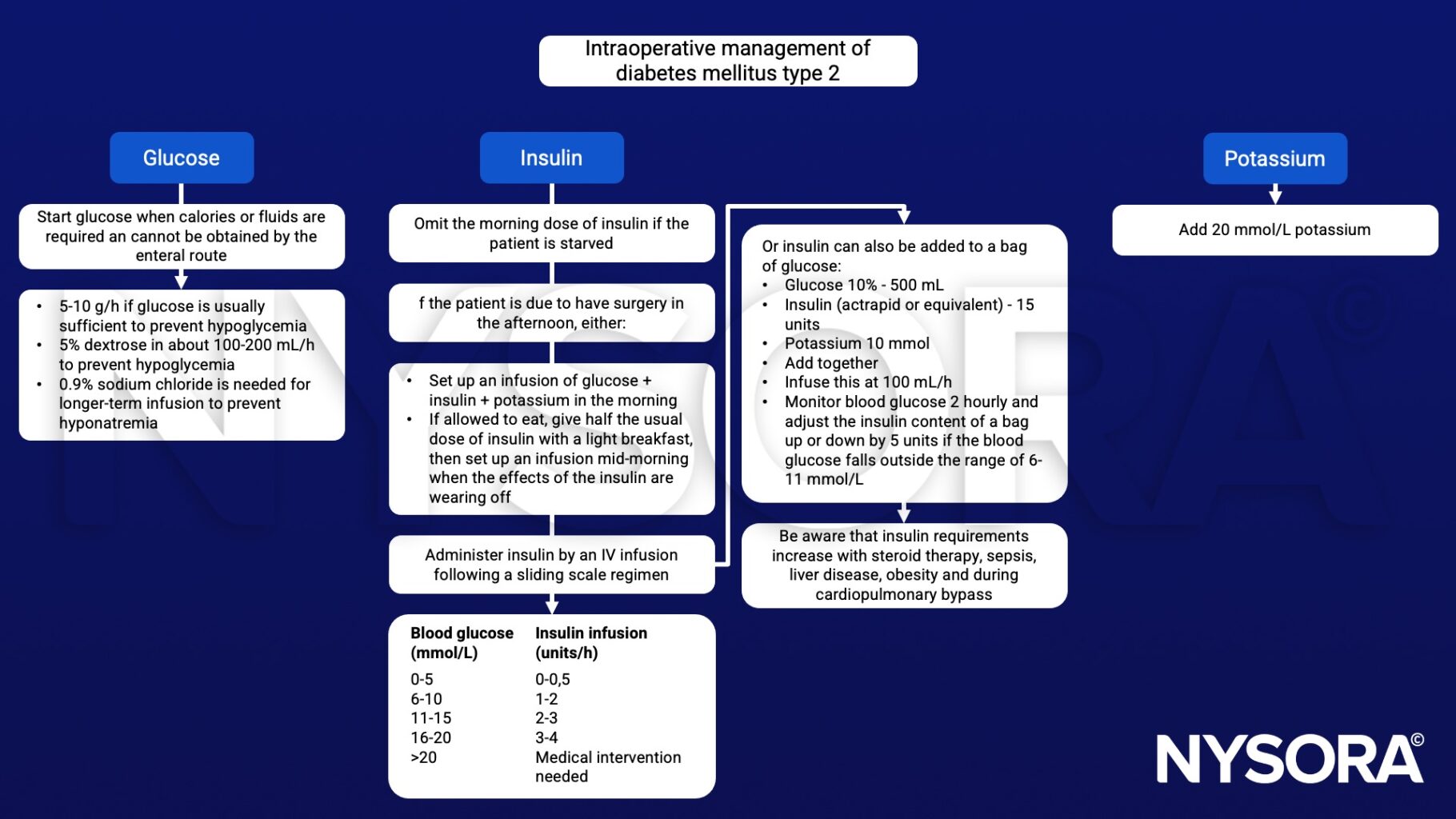
Perioperative management
Postoperative care
- Check blood glucose levels hourly until a normal diet is established
- Monitor plasma potassium 3-4 hourly, or more frequently if clinically indicated
- Administer appropriate analgesia
- Use NSAIDs with great caution as they may further impair renal function in patients with a nephropathy
- Avoid dexamethasone as it exacerbates insulin resistance
Keep in mind
HbA1c has a strong predictive value for complications of diabetes
Suggested reading
- Pollard BJ, Kitchen, G. Handbook of Clinical Anaesthesia. Fourth Edition. CRC Press. 2018. 978-1-4987-6289-2.
- Pontes JPJ, Mendes FF, Vasconcelos MM, Batista NR. Avaliação e manejo perioperatório de pacientes com diabetes melito. Um desafio para o anestesiologista [Evaluation and perioperative management of patients with diabetes mellitus. A challenge for the anesthesiologist]. Braz J Anesthesiol. 2018;68(1):75-86.
- Cornelius BW. Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: Anesthetic Management in the Ambulatory Setting: Part 2: Pharmacology and Guidelines for Perioperative Management. Anesth Prog. 2017;64(1):39-44.
- Stubbs, D.J., Levy, N., Dhatariya, K., 2017. Diabetes medication pharmacology. BJA Education 17, 198–207.
- Nicholson G, Hall GM. 2011. Diabetes and adult surgical inpatients. Continuing Education in Anaesthesia Critical CAre & Pain. 11;6:234-238.
- Robertshaw HJ, Hall GM. Diabetes mellitus: anaesthetic management [published correction appears in Anaesthesia. 2007 Jan;62(1):100]. Anaesthesia. 2006;61(12):1187-1190.
- McAnulty GR, Robertshaw HJ, Hall GM. Anaesthetic management of patients with diabetes mellitus. Br J Anaesth. 2000;85(1):80-90.
We would love to hear from you. If you should detect any errors, email us customerservice@nysora.com