Learning objectives
- Describe Ehlers Danlos syndrome
- Recognize the symptoms and signs of Ehlers Danlos syndrome
- Anesthetic management of a patient with Ehlers Danlos syndrome
Definition and mechanisms
- Ehlers Danlos syndrome (EDS) comprises a group of clinically and genetically heterogeneous heritable connective tissue disorders, characterized by joint hypermobility and instability, skin texture anomalies, and vascular and internal organ fragility
- Clinical manifestations range from extremely mild phenotypes to life-threatening complications depending on the specific subtype
- The current Villefranche nosology recognizes six major subtypes, comprising classic, hypermobile, vascular, kyphoscoliotic, arthrochalasia, and dermatosparaxis, most of which are linked to mutations in one of the genes encoding for fibrillar collagen proteins or enzymes involved in post-translational modification of these proteins
| Common subtype | Major criteria | Minor criteria | Inheritance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Classic | Skin hyperextensibility Widened atrophic scars Joint hypermobility | Smooth, velvety skin Mulluscoid pseudotumors Subcutaneous spheroids Complications of joint hypermobility Muscle hypotonia, motor delay Easy bruising Manifestations of tissue extensibility and fragility Surgical complications Positive family history | AD |
| Hypermobility | Hyperextensible and/or smooth, velvety skin Generalized joint hypermobility | Recurring joint dislocations Chronic joint/limb pain Positive family history | AD (?) |
| Vascular | Thin, translucent skin Arterial/intestinal/uterine fragility or rupture Extensive bruising Characteristic facial appearance | Acrogeria Hypermobility of small joints Tendon and muscle rupture Talipes equinovarus Early-onset varicose veins Arteriovenous, carotid-cavernous sinus fistula Pneumothorax/pneumohemothorax Gingival recessions Positive family history, sudden death in a close relative | AD |
| Kyphoscoliotic | Generalized joint hypermobility Congenital hypotonia Congenital and progressive scoliosis Scleral fragility and rupture of the ocular globe | Tissue fragility, including atrophic scars Easy bruising Arterial rupture Marfanoid habitus Microcornea Osteopenia, -porosis Positive family history | AR |
| Arthrochalasis | Generalized joint hypermobility with recurrent subluxations Congenital bilateral hip dislocation | Skin hyperextensibility Tissue fragility, including atrophic scars Easy bruising Hypotonia Kyphoscoliosis Osteopenia, -porosis | AD |
| Dermatosparaxis | Severe skin fragility Sagging, redundant skin | Soft, doughy skin texture Easy bruising Premature rupture of fetal membranes Large hernias (umbilical, inguinal) | AR |
AD, autosomal dominant; AR, autosomal recessive.
Signs and symptoms
- Loose joints
- Joint pain
- Stretchy, velvety skin
- Fragile skin
- Abnormal scar formation
Complications
- Aortic dissection
- Joint dislocations
- Scoliosis
- Chronic pain
- Early osteoarthritis
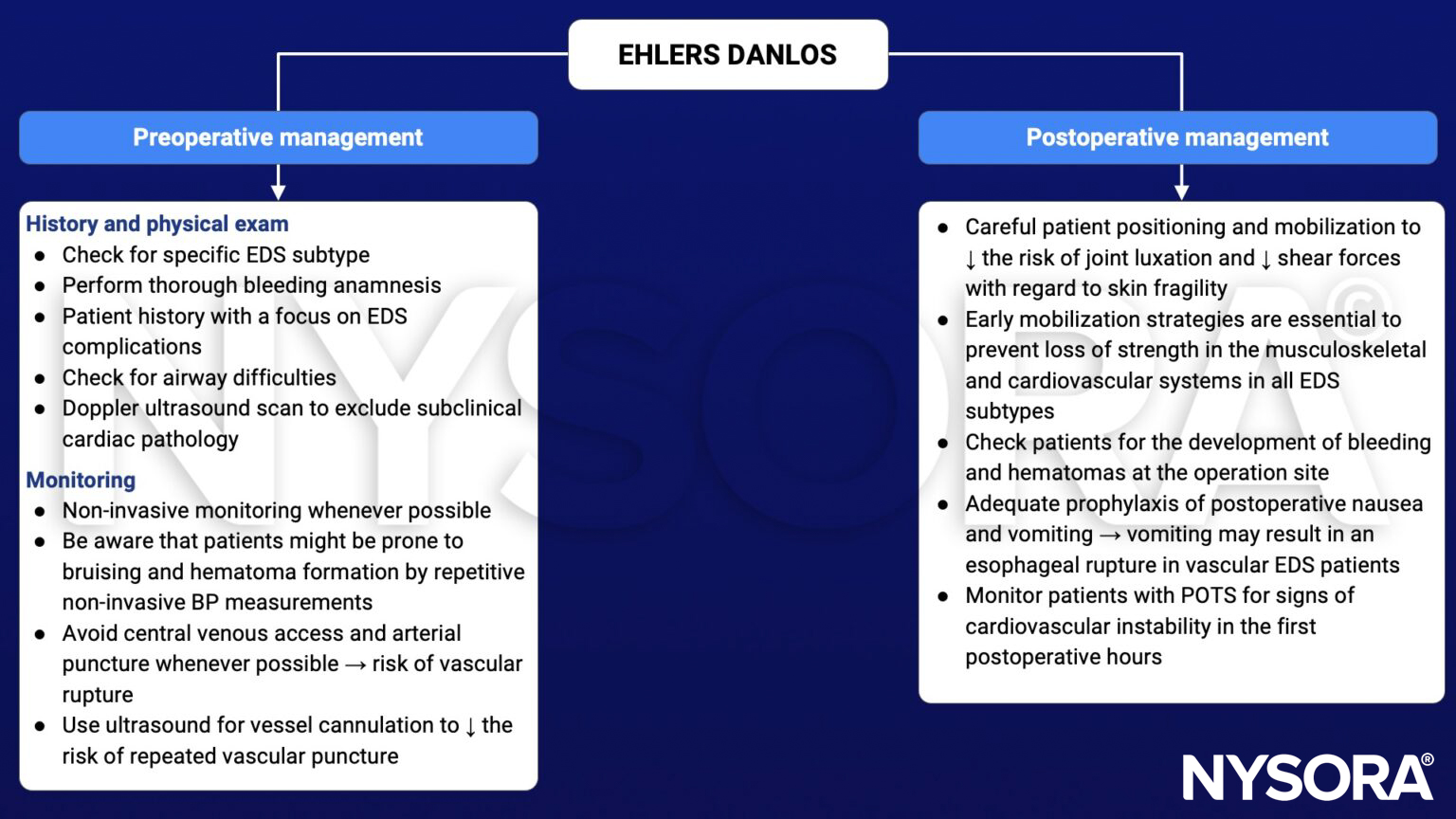
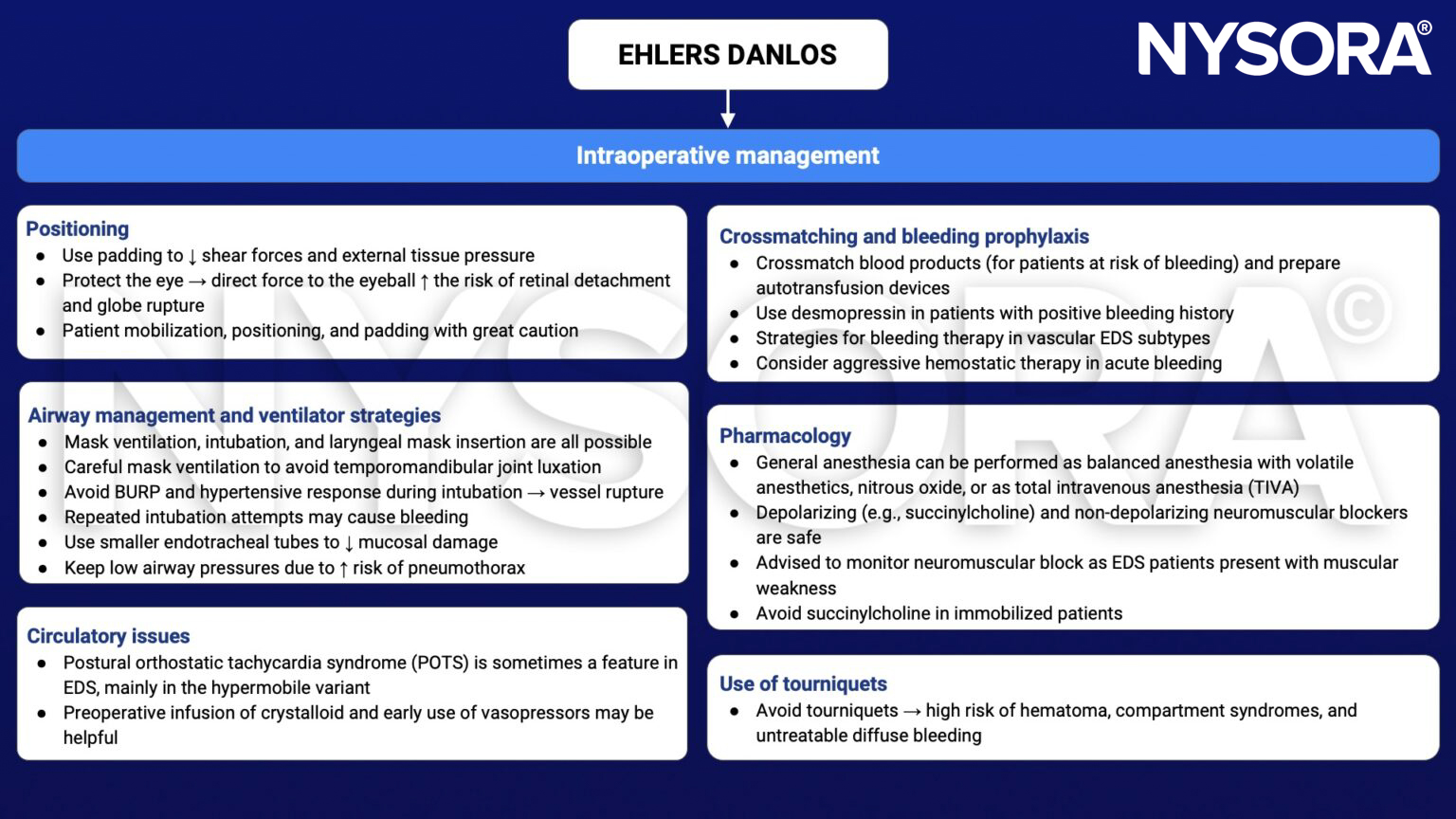
Management
Obstetrical anesthesia
- Difficult management, requires multidisciplinary effort
- High risk of preterm labor, uterine rupture, and hemorrhage
- Neuraxial anesthesia is relatively contraindicated, may need general anesthesia
- If vascular subtype → recommendations are termination of pregnancy or Cesarean section before 32 weeks
Keep in mind
- Avoid ambulatory surgery in EDS patients
- Be aware of typical EDS-related emergency-like situations such as difficult airway status, bleeding risks, and organ rupture in specific subtypes
Suggested reading
- Malfait F, Francomano C, Byers P, et al. The 2017 international classification of the Ehlers-Danlos syndromes. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2017;175(1):8-26.
- Wiesmann T, Castori M, Malfait F, Wulf H. Recommendations for anesthesia and perioperative management in patients with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome(s). Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2014;9(109).