Learning objectives
- Describe Goldenhar syndrome
- Understand how Goldenhar syndrome affects the airway
- Discuss the perioperative management of patients with Goldenhar syndrome
Definition and mechanisms
- Goldenhar syndrome (GS), also called oculo-auriculo-vertebral syndrome or hemifacial microsomia, is a rare disorder of craniofacial development
- Congenital malformation of the first and second branchial arches, resulting in the incomplete development of the ear, nose, soft palate, lip, and mandible (usually unilateral)
- It is characterized by the triad of mandibular hypoplasia resulting in facial asymmetry, ear and/or eye malformation, and vertebral anomalies
- Patients can also present with heart, kidney, and lung malformations, and central nervous system defects
- Male-to-female ratio 3:2
Signs and symptoms
- Mandibular hypoplasia (facial asymmetry)
- Eye anomalies: Microphthalmia, anophthalmia, epibulbar dermoids, and eyelid colobomas
- Ear anomalies: Preauricular tags, anotia (totally absent ear), and microtia (partially formed ear)
- Vertebral anomalies: Scoliosis, kyphosis, hemivertebrae, and cervical fusion
- Cleft lip and/or palate
- Wider than normal mouth
- Hydrocephalus
- Congenital heart defects in ⅓ of patients (most commonly septal and conotruncal defects, e.g., tetralogy of Fallot)
- Genitourinary malformations (e.g., ectopic or fused kidneys, renal agenesis, ureteropelvic junction obstruction, or vesicoureteral reflux)
- Partial or complete unilateral lung hypoplasia
- Developmental delay and autism spectrum disorder in some patients
Complications
- Vision problems and/or loss
- Hearing loss
- Feeding difficulties
- Speech difficulties
- Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA)
- Strabismus
- Pulmonary hypoplasia might increase the risk for respiratory infections, pulmonary hypertension, and pneumothorax
- Severe spinal deformities might cause restrictive lung disease and further decrease pulmonary function
Treatment
- Eyeglasses or surgery to improve vision
- Hearing aids or bone-anchored auditory implants
- Feeding assistance with special bottles or nasogastric feedings
- Speech therapy to increase language and communication skills
- Reconstructive surgery
- Surgery to correct a congenital heart defect, cleft lip or palate, obstructive sleep apnea, microtia, or spinal defect
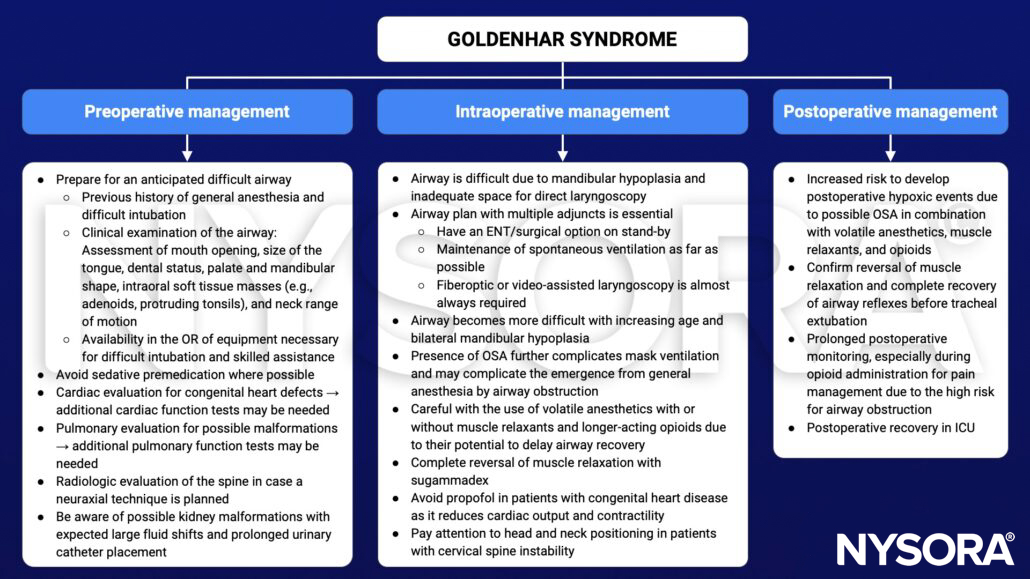
Management
Suggested reading
- Sun YH, Zhu B, Ji BY, Zhang XH. Airway Management in a Child with Goldenhar Syndrome. Chin Med J (Engl). 2017;130(23):2881-2882.
- Goldenhar Syndrome. In: Bissonnette B, Luginbuehl I, Marciniak B, Dalens BJ. eds. Syndromes: Rapid Recognition and Perioperative Implications. McGraw Hill; 2006. Accessed February 09, 2023. https://accessanesthesiology.mhmedical.com/content.aspx?bookid=852§ionid=49517623
- Kaymak C, Gulhan Y, Ozcan AO, Baltaci B, Unal N, Safak MA, Oguz H. Anaesthetic approach in a case of Goldenhar’s syndrome. European Journal of Anaesthesiology. 2022; 19(11):836-838.