Learning objectives
- Describe hyperparathyroidism
- Recognize the symptoms and signs of hypercalcemia, related to hyperparathyroidism
- Anesthetic management of a patient with hyperparathyroidism
Definition and mechanisms
- Hyperparathyroidism (HPT) is a condition in which the parathyroid glands produce too much parathyroid hormone (PTH)
- PTH plays an important role in maintaining normal calcium homeostasis
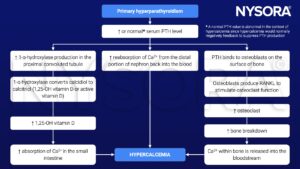
- The main effector sites responding directly or indirectly to PTH are the intestines, kidneys, and bone
- HPT ultimately results in hypercalcemia
Classification
- Primary HPT: Hyperfunction of the parathyroid glands (i.e., adenoma, carcinoma, or hyperplasia) leading to an overproduction of PTH
- Secondary HPT: Appropriate compensatory response of the parathyroid glands to secrete more PTH in response to a condition (i.e., chronic kidney disease, vitamin D deficiency) that produces hypocalcemia
- Tertiary HPT: Long-standing secondary HPT starts to behave like primary HPT, usually associated with advanced kidney failure
- Ectopic HPT: Secretion of PTH by tissues other than the parathyroid glands
Signs and symptoms
The symptoms of HPT are caused by hypercalcemia:
- Cardiovascular: Hypertension, shortened QT interval, prolonged PR interval, hypovolemia, conduction blockade
- Neurological: Mental status changes, weakness, lethargy
- Respiratory: Potential respiratory muscle weakness, poor clearance of secretions
- Musculoskeletal: Muscle weakness, osteoporosis, pathological fractures, bone pains
- Gastrointestinal: Abdominal pain, peptic ulcer, pancreatitis, nausea/vomiting, ↑ aspiration risk
- Renal: Polyuria, polydipsia, renal stones, renal failure
- Hematopoietic: Anemia
Risk factors
- Age: Older adults (>60 years)
- Sex: Female sex
- Genetic conditions: Multiple endocrine neoplasia syndromes (MEN)
Pathophysiology
Treatment
- Primary HPT: Parathyroidectomy
- Secondary HPT: Treat underlying cause (i.e., chronic kidney failure, vitamin D deficiency)
- Tertiary HPT: Parathyroidectomy
- Calcimimetics are used in patients with primary HPT unable to undergo parathyroidectomy and for patients with secondary HPT on dialysis
Management

Suggested reading
- Malhotra S, Sodhi V. Anaesthesia for thyroid and parathyroid surgery. Continuing Education in Anaesthesia Critical Care & Pain. 2007;7(2):55-58.
We would love to hear from you. If you should detect any errors, email us [email protected]