Learning objectives
- Describe the definition and possible causes of massive hemoptysis
- Diagnose massive hemoptysis
- Manage massive hemoptysis occurrence
Definition & mechanisms
- Hemoptysis is defined as the expectoration of blood originating from the lower respiratory tract
- There is no agreed definition of massive hemoptysis, with volumes ranging from 100 mL to 1000 mL within 24 hours
- In practice, life-threatening hemoptysis occurs with any volume of blood that could obstruct the airway or cause significant hemodynamic compromise
- Emergency that requires prompt management
Pathophysiology
- In 90% of cases, the source is the bronchial circulation
- causes:
Infectious Mycobacteria
Fungal infections (mycetomas)
Necrotizing pneumonia and lung abscess (Klebsiella, Pseudomonas, Streptococcus, Actinomyces)
Bacterial endocarditis with septic emboli
Parasitic (paragonimiasis, hydatid cyst)
Parasitic (paragonimiasis, hydatid cyst) Bronchogenic carcinoma
Endobronchial tumors (carcinoid, adenoid cystic carcinoma)
Pulmonary metastases
Sarcoma
Pulmonary Bronchiectasis (including cystic fibrosis)
Chronic bronchitis
Alveolar hemorrhage and underlying causes
Diffuse alveolar damage
Cardiac/pulmonary vascular Pulmonary artery aneurysm (rasmussen aneurysm, mycotic, arteritis)
Bronchial artery aneurysm
Pulmonary infarct (embolism)
Pulmonary hypertension
Congenital cardiac or pulmonary malformations
Airway-vascular fistulae
Arteriovenous malformations
Mitral stenosis
Left-ventricular failure
Pulmonary veno-occlusive disease
Vasculitis/collagen vascular disease Granulomatosis with polyangiitis
Goodpasture’s syndrome
Behçet’s disease
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Essential mixed cryoglobulinemia
Henoch-Schonlein purpura
Mixed connective tissue disease
Progressive systemic sclerosis
Rheumatoid arthritis
Systemic necrotizing vasculitis
Immune complex associated glomerulonephritis
Pauci-immune glomerulonephritis
Hematologic Coagulopathy (congenital, acquired or iatrogenic)
Platelet disorders
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
Drugs and toxins Penicillamine
Solvents
Crack cocaine
Trimellitic anhydride
Bevacizumab
Isocyanates
Nitrofurantoin
Trauma Catheter-induced pulmonary artery rupture
Blunt or penetrating chest injury
Transtracheal procedures
Iatrogenic secondary to interventional pulmonology procedures
Bronchoscopic biopsy
Miscellaneous Cryptogenic
Endometriosis
Lymphangiolyomyomatosis
Broncholithiasis
Foreign body aspiration
Lung transplantation
Tuberous sclerosis
Idiopathic pulmonary hemosiderosis
Diagnosis
- The main goals are identifying the site of bleeding and revealing the underlying cause
- Diagnostic tools:
- Chest radiography
- Computed tomography
- Fiberoptic bronchoscopy
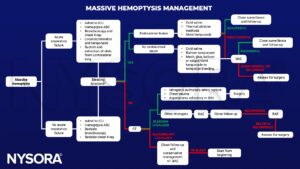
Management
- Hemoptysis ABCs:
- Bleeding side down (if known bleeding site)
- Intubation
-
-
- Rigid intubation
- Single-lumen endotracheal intubation
-
-
- Contralateral isolation and single-lung ventilation
- Volume resuscitation (crystalloids/colloids)
- Multidisciplinary call/page
- Interventional radiology
- ICU
- Interventional pulmonology
- Anesthesiology
- Surgery: Lung resection
Suggested reading
- Radchenko C, Alraiyes AH, Shojaee S. A systematic approach to the management of massive hemoptysis. J Thorac Dis. 2017;9(Suppl 10):S1069-S1086.
- Thomas, A. and Lynch, G. (2011) Management Of Massive Haemoptysis, WFSA. Available at: https://resources.wfsahq.org/atotw/management-of-massive-haemoptysis/ (Accessed: January 23, 2023).
We would love to hear from you. If you should detect any errors, email us [email protected]