Learning objectives
- Diagnose and treat MDMA toxicity
Definitions and mechanisms
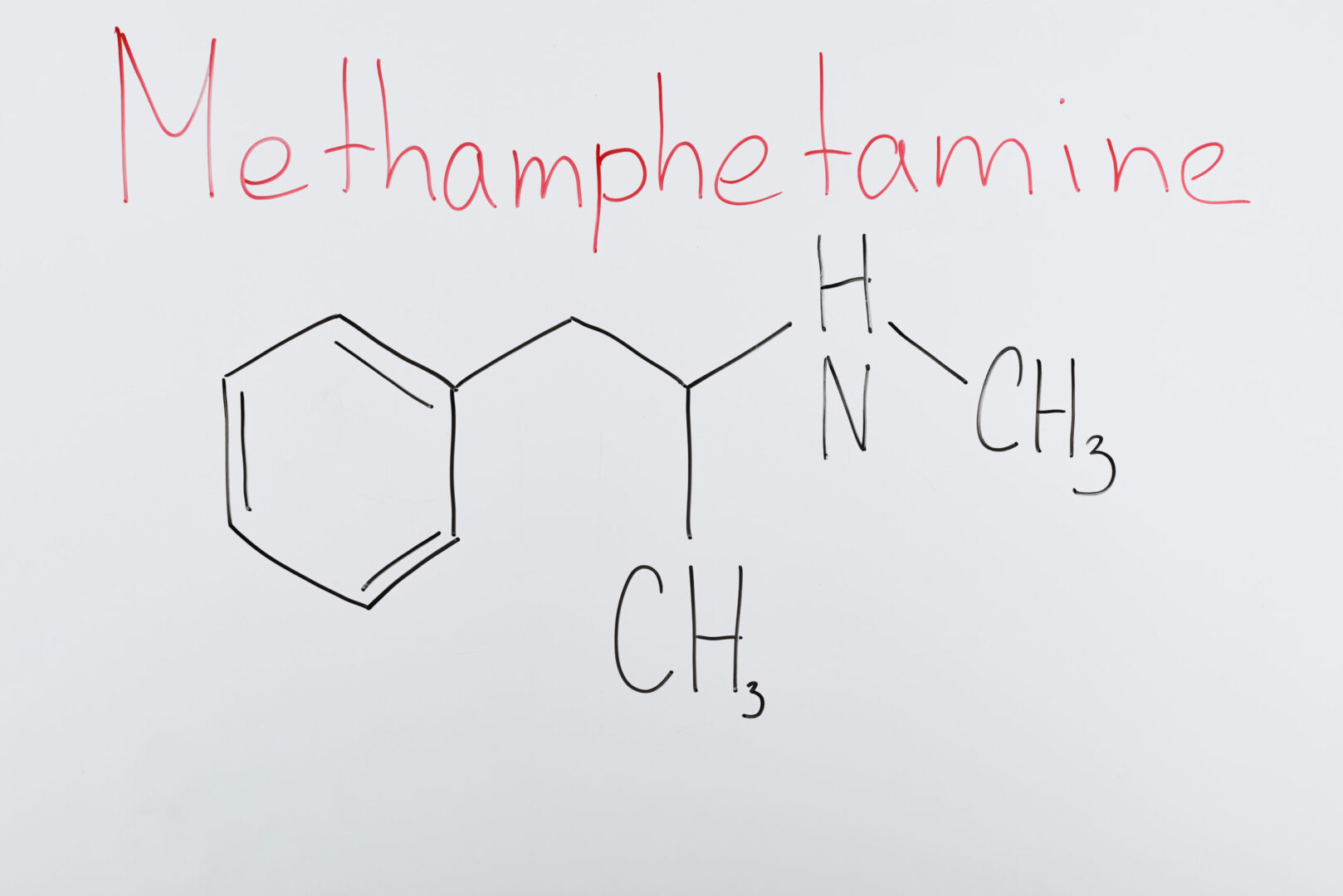
- MDMA (3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine) ecstasy is a synthetic compound with structural and pharmacologic similarities to both amphetamines and mescaline
- Typical effects include feelings of euphoria, wakefulness, intimacy, excitement, and a loss of inhibitions
- It is mistakenly believed that it is a safe drug with little toxicity and a long duration of action
- The effects of MDMA typically last anywhere from 3 to 6 hours
- Effects are thought to result from alterations in serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine
- The drug is commonly ingested orally in tablet form, however, the powder itself can be snorted
- Absorbed via the GI tract with an onset of effect between 20 minutes and 1 hour after consumption
- MDMA is profoundly serotonergic and can precipitate serotonin syndrome
Side effects associated with MDMA
| Minor side effects | Life-threatening side effects |
|---|---|
| Trismus | Hyperpyrexia > 41.5°C |
| Tachycardia | Rhabdomyolysis |
| Bruxism | Serotonin syndrome |
| Anxiety | Acute liver failure |
| Prolonged hangover | Hyponatremia and cerebral edema |
Signs and symptoms
| System | Minor or moderate overdose | Severe overdose |
|---|---|---|
| Cardiovascular | Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC) Intracranial hemorrhage Severe Hypotension or Hypertension Hypotensive bleeding |
|
| Central nervous system | Hyperreflexia Agitation Mental confusion Paranoia Stimulant psychosis | Cognitive and memory impairment potentially to the point of retrograde or anterograde amnesia Coma Convulsions Hallucinations Loss of consciousness Serotonin syndrome |
| Musculoskeletal | Muscle rigidity Rhabdomyolysis |
|
| Respiratory | Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome | |
| Urinary | Acute kidney injury (AKI) | |
| Other | Cerebral edema Hepatitis Hyperpyrexia Hyponatremia |
Complications
- Neurological
- Cardiovascular
- Cardiac dysrhythmias
- Myocardial infarction
- Aortic dissection
- Intracranial hemorrhages
- GI
- Hepatotoxicity
- Liver failure
- Renal
- Rhabdomyolysis
- Acute renal failure
- Endocrine
- SIADH resulting in life-threatening hyponatremia
- Minor complications
- Increased muscle activity (such as bruxism, restless legs, and jaw clenching)
- Hyperactivity
- Insomnia
- Difficulty concentrating
- Feelings of restlessness
Risk factors
- Ingestion of several doses at once or in a short period
- Mixing MDMA with alcohol or other drugs
- Vigorous physical activity
- Use of MDMA in a hot environment
Diagnosis
- Blood glucose levels
- Electrolyte abnormalities
- Urine, potassium, BUN, creatinine, creatine phosphokinase levels, and myoglobin levels for the evaluation of rhabdomyolysis and renal injury
- LFTs for hepatotoxicity
- Aspirin, alcohol, acetaminophen levels, and urine drug screening
- ECG
- Head CT, lumbar punction
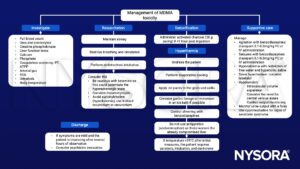
Management
Suggested reading
- Davies N, English W, Grundlingh J. MDMA toxicity: management of acute and life-threatening presentations. Br J Nurs. 2018;27(11):616-622.
- Nicholson Roberts, T., Thompson, J.P., 2013. Illegal substances in anaesthetic and intensive care practices. Continuing Education in Anaesthesia Critical Care & Pain 13, 42–46.
- Hall, A.P., Henry, J.A., 2006. Acute toxic effects of ‘Ecstasy’ (MDMA) and related compounds: overview of pathophysiology and clinical management. British Journal of Anaesthesia 96, 678–685.
We would love to hear from you. If you should detect any errors, email us customerservice@nysora.com