Learning objectives
- Know the challenges in the perioperative management of these patients
- Recognise a myasthenic or cholinergic crisis
Definition and mechanisms
- Myasthenia Gravis (MG) is an autoimmune disease of the neuromuscular junction at the postsynaptic membrane
- Autoantibodies to AchR disrupt its function by receptor blockade and conformational change leading to increased degradation which results in decreased motor end-plate potential amplitude and failure in the initiation of muscle contraction
- It is the most common disorder of the neuromuscular junction
Signs and symptoms
- Muscle weakness and fatigue of:
| Extraocular muscle group | Ptosis Diplopia |
| Bulbar muscle group | Dysarthria Dysphagia Dysphonia |
| Axial-limb muscle group | Symmetrical, more often in proximal muscles |
| Respiratory muscles | Dyspnea |
- Symptoms vary over the day and from day to day, often with normal or near-normal muscle strength in the morning
- Clinical presentation varies from mild and localized to severe, generalized weakness of multiple muscle groups
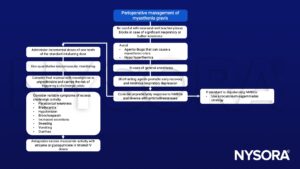
Myasthenic crisis is a life-threatening condition in which severe respiratory muscle insufficiency leads to respiratory failure
- Precipitants
- Infection
- Surgery
- Residual neuromuscular block
- Pain
- Hypo- and hyperthermia
- Reduction or withdrawal of treatment
- Pregnancy
- Stress
- Sleep deprivation
- Agents/drugs:
| Antibiotics | Aminoglycoside Fluoroquinolones Tetracycline Macrolides Sulfonamides Penicillin Vancomycin Clindamycin Ketolides |
| Non-depolarizing neuromuscular-blocking agents | Pancuronium Vecuronium Atracurium |
| Cardiovascular agents | Beta-blockers Calcium channel blockers Procainamide Quinidine Beryllium |
| Anesthetic agents | Local: procaine, lidocaine, bupivacaine Inhalation: halothane, isoflurane Neuromuscular blockers |
| Anticonvulsants | Carbamazepine Gabapentine Phenobarbital Phenytoin Ethosuximide |
| Other agents | Botulinum toxin Chloroquine Hydroxychloroquine Magnesium Penicillamine Quinine Iodinated contrast agents Cisplatinum Riluzole Interferon-alfa Interleukin-2 |
Treatment
- Respiratory support
- Urgent neurological input
- High-dose steroids/intravenous immunoglobulins
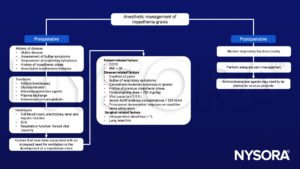
Anesthetic management
Suggested reading
- P. Daum, J. Smelt and I.R. Ibrahim. Perioperative management of myasthenia gravis. 2021, BJA Education, 21(11): 414-429.
- Dhallu MS, Baiomi A, Biyyam M, Chilimuri S. Perioperative Management of Neurological Conditions. Health Serv Insights. 2017;10:1178632917711942.
- Dillon FX. Anesthesia issues in the perioperative management of myasthenia gravis. Semin Neurol. 2004;24(1):83-94.
We would love to hear from you. If you should detect any errors, email us customerservice@nysora.com


