Learning objectives
- Optimize blood hemoglobin levels to avoid or minimize transfusion necessity during surgery
Definition
- Anemia is a condition in which the number of red blood cells or the hemoglobin concentration within them is lower than normal
- Hemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells (RBCs) and is responsible for transporting oxygen from the lungs to tissues and organs
- Normal blood hemoglobin levels range from:
- 13.8 – 17.2 g/dL in men
- 12.1 – 15.1 g/dL in women
Signs and symptoms
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath
- Paleness
- Resting tachycardia
Note that these symptoms are unreliable as people with long-existing anemia might be asymptomatic
Causes and classification
- Anemia is classified depending on the size of the RBCs
| Microcytic (MCV <80 fL) | Normocytic | Macrocytic MCV >100 fL | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Causes | Iron deficiency Thalassemia Anemia of inflammation Sideroblastic anemia | Acute bleeding Renal disease Acute inflammation | Vitamin B12 deficiency Folate deficiency Myelodysplastic syndrome Chemotherapy Aplastic anemia Liver and renal disease Hypothyroidism Reticulocytosis |
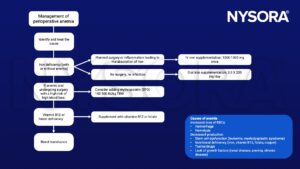
Management
Suggested reading
- Hare GMT, Mazer CD. Anemia: Perioperative Risk and Treatment Opportunity. Anesthesiology. 2021;135(3):520-530.
- Cascio MJ, DeLoughery TG. Anemia: Evaluation and Diagnostic Tests. Med Clin North Am. 2017;101(2):263-284.
- Chernecky CC et al. Laboratory Tests and Diagnostic Procedures. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2013:621-623.
We would love to hear from you. If you should detect any errors, email us customerservice@nysora.com