Learning objectives
- Definition of placenta accreta spectrum
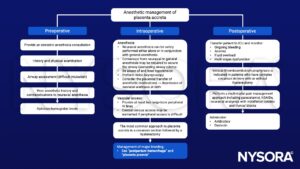
- Anesthetic management of placenta accreta
Definition and mechanisms
- Refers to a severe pregnancy complication that occurs when the placenta grows too deeply into the uterine wall
- With placenta accreta, part or all of the placenta remains attached after delivery, thereby possibly leading to severe blood loss after delivery
- Is considered a high-risk pregnancy complication
- Three types:
- Placenta accreta:
- Placental villi adhere to the myometrium
- Placenta does not pass through the wall of the uterus and does not impact the uterine muscles
- Majority of cases
- Placenta increta:
- Invasion of the myometrium
- Placenta does not pass through the uterine wall
- 15-18% of cases
- Placenta percreta:
- Invasion through the myometrium to the serosa and surrounding organs
- Might impact other organs such as the bladder or intestines
- Most severe
- 5-7% of cases
- Placenta accreta:
Signs and symptoms
- Often no signs or symptoms
- Although vaginal bleeding during the third trimester might occurs
Risk factors
- Previous uterine surgery or caesarean section
- Placenta position: if the placenta partially or totally covers the cervix (placenta previa) or sits in the lower portion of the uterus
- Maternal age > 35 years
- Multiparity
- IVF
Complications
- Major vaginal bleeding
- Thromboembolism
- Coagulopathy
- Anemia
- Premature birth
- Amniotic fluid embolism
- Damage to the uterus and surrounding organs
- Loss of fertility due to a hysterectomy
- Acute transfusion reaction
- Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)
- Acute kidney injury
- Infection
- Multisystem organ failure
Diagnosis
- Ultrasound
- MRI
Management
- Planning for delivery
- Obstetricians will plan delivery between 35+0 and 36+6 weeks gestation in women stringy suspected to have placenta accreta
- Administer a single course of antenatal glucocorticoids between 34 and 36 weeks of gestation
- Symptoms of bleeding or preterm labor may hasten the need for delivery
Suggested reading
- Reale, S.C., Farber, M.K., 2022. Management of patients with suspected placenta accreta spectrum. BJA Education 22, 43–51.
- Silver RM, Barbour KD. Placenta accreta spectrum: accreta, increta, and percreta. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2015;42(2):381-402.
We would love to hear from you. If you should detect any errors, email us customerservice@nysora.com