Learning objectives
- Describe rheumatoid arthritis
- Recognize the symptoms and signs of rheumatoid arthritis
- Anesthetic management of a patient with rheumatoid arthritis
Definition and mechanisms
- Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune inflammatory disorder that mainly affects the synovial joints → symmetrical erosive polyarthropathy
- Early RA affects the smaller joints first (hands and feet)
- As RA progresses, symptoms spread to the wrists, knees, ankles, elbows, hips, and shoulders
- Periods of increased disease activity (flares) alternate with periods of relative remission
- RA also affects other organs in more than 15-25% of the cases → systemic
Signs and symptoms
- Tender, warm, swollen joints
- Joint stiffness that is usually worse in the mornings and after inactivity
- Fatigue, fever, loss of appetite
- The painful swelling can eventually result in bone erosion and joint deformity
Risk factors
- Female gender
- Family history
- Increasing age
- Smoking
- Overweight
Complications
- Osteoporosis
- Rheumatoid nodules
- Dry eyes and mouth (Sjogren’s syndrome)
- Infections
- Abnormal body composition
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Cardiovascular disease
- Lung disease
- Lymphoma
Extra-articular manifestations
- Neurological: Central neuropathy, peripheral neuropathy (carpal tunnel syndrome), autonomic neuropathy
- Ocular: Kerato-conjuctivitis
- Cardiovascular: Pericarditis, pericardial effusion, cardiac tamponade, valvular heart disease (usually regurgitation), conduction abnormalities, granulomatous disease, endocarditis or myocarditis, coronary artery disease
- Respiratory: Reduced chest wall compliance (costochondral disease), pleural effusion, restrictive lung disease, pulmonary nodule
- Hematological: Anemia [chronic disease, iron deficiency (bleeding) and bone marrow suppression from medication], thrombocytopenia, Felty’s syndrome, lymphoma
- Hepatic: Hepatic fibrosis, hepatomegaly with splenomegaly, hypoalbuminemia
- Renal: Glomerulonephritis, tubulointerstitial nephritis, amyloidosis
- Skin: Fragile skin, pyoderma gangrenosum, Sicca syndrome, scleritis, scleromalacia perforans
- Musculoskeletal: Osteoporosis
Treatment
- Medications: Relieve pain, reduce inflammation, slow down the progression of RA
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Ibuprofen and naproxen
- Corticosteroids: Prednisone
- Conventional disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs): Methotrexate, leflunomide, hydroxychloroquine, and sulfasalazine
- Biological DMARDs: Abatacept, adalimumab, anakinra, certolizumab, etanercept, golimumab, infliximab, rituximab, sarilumab, and tocilizumab
- Targeted synthetic DMARDs: Baricitinib, tofacitinib, and upadacitinib
- Physical therapy: To reduce pain and stiffness
- Surgery: Repair damaged joints to restore function and reduce pain
-
- Synovectomy
- Tendon repair
- Joint fusion
- Total joint replacement
Management
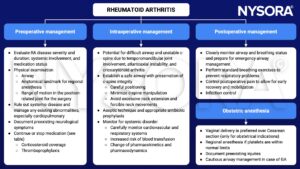
Recommendations on how to deal with RA medications during elective surgical procedures
| Medication | Administration during surgical procedure |
|---|---|
| Corticosteroids | See next table |
| Conventional DMARDs | Continue |
| Biologic DMARDs | Withhold before surgery and schedule surgery at the end of the dosing cycle |
| Targeted synthetic DMARDs | Withhold at least 7 days prior to surgery |
Recommended steroid doses during surgery
| Type of surgery | Endogenous cortisol secretion rate | Examples | Recommended steroid dosing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Superficial | 8-10 mg/day (baseline) | Dental surgery, biopsy | Usual daily dose |
| Minor | 50 mg/day | Inguinal hernia, colonoscopy, uterine curettage, hand surgery | Usual daily dose plus hydrocortisone 50 mg i.v. before incision + hydrocortisone 25 mg i.v. every 8 hrs for 1 day + usual daily dose |
| Moderate | 75-150 mg/day | Low extremity revascularization, total joint replacement, cholecystectomy, colon cancer, abdominal hysterectomy | Usual daily dose plus hydrocortisone 50 mg i.v. before incision + hydrocortisone 25 mg i.v. every 8 hrs for 1 day + usual daily dose |
| Major | 75-150 mg/day | Esophagectomy, total proctocolectomy, major cardiac/vascular surgery, hepaticojejenostomy, delivery, trauma | Usual daily dose plus hydrocortisone 100 mg i.v. before incision + continuous i.v. infusion of hydrocortisone 200 mg for >1 day or hydrocortisone 50 mg i.v. every 8 hours/day + taper dose by half/day until usual daily dose reached and continuous i.v. fluids with 5% dextrose and 0.2-0.45% sodium chloride, based on degree of hypoglycemia |
Keep in mind
- Carefully perform a preoperative evaluation to prevent complications and minimize injury
- Anesthetic management strategies should consider RA-related systemic problems
- Individualize postoperative management
Suggested reading
- Kim HR, Kim SH. Perioperative and anesthetic management of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Korean J Intern Med. 2022;37(4):732-739.
- Samanta R, Shoukrey K, Griffiths R. Rheumatoid arthritis and anaesthesia. Anaesthesia. 2011;66(12):1146-1159.
We would love to hear from you. If you should detect any errors, email us customerservice@nysora.com