A 56-year-old male with diabetes presented with a six-month history of chronic right shoulder pain. The patient complained of night pain, increasing severity of pain, limited painful abduction up to 45 degrees, and increased stiffness. Due to the restricted range of motion, determination of the presence of a painful arc was not possible.
Physical examination
- Painful global restriction of movements, particularly abduction and external rotation
- Acromioclavicular joint tenderness
- Specific clinical tests were not possible due to the global restriction of movement
Ultrasound findings
- Rotator cuff arthropathy: Supraspinatus tendon tears
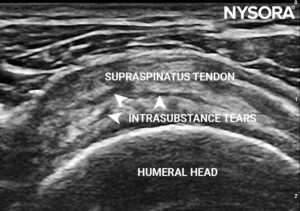
Short axis view of the rotator cuff showing intrasubstance tears in the supraspinatus tendon.
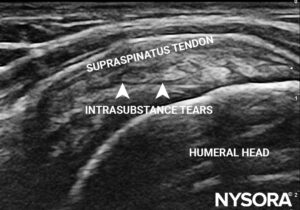
Long axis view of the rotator cuff showing intrasubstance tears in the supraspinatus tendon.
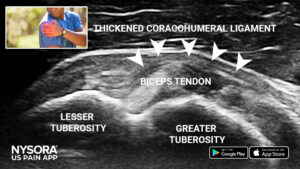
- Coracohumeral ligament thickening
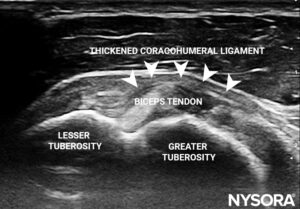
Axial view of the shoulder showing thickening of the coracohumeral ligament over the intra-articular portion of the biceps tendon.
- Neoangiogenesis around the biceps tendon
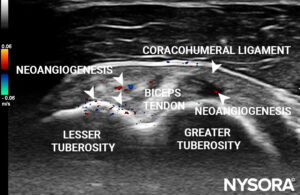
Color Doppler imaging revealed neoangiogenesis around the biceps tendon.
- Posterior capsular thickening
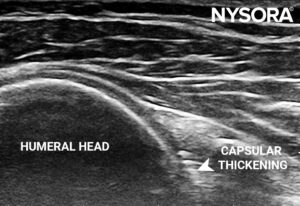
Examination of the posterior glenohumeral joint recess revealing capsular thickening.
- Distended acromioclavicular joint
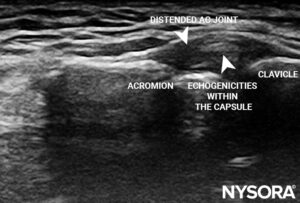
Transverse view of the acromioclavicular (AC) joint showing a distended joint with echogenicities within the capsule.
Diagnosis
The patient was diagnosed with adhesive capsulitis secondary to rotator cuff tendinopathy. Adhesive capsulitis, commonly referred to as frozen shoulder, is an inflammatory condition in which the body forms excessive scar tissue or adhesions across the glenohumeral joint, resulting in pain, stiffness, and reduced range of motion. Certain risk factors, such as diabetes, previous shoulder injuries, and thyroid disorders, increase the likelihood of developing adhesive capsulitis.
To read more about the treatment, patient outcome, and other case studies, download the most practical app on ultrasound-guided chronic pain blocks for the management of chronic pain HERE.