Understanding vascular anatomy: How to distinguish between veins and arteries
May 23, 2024
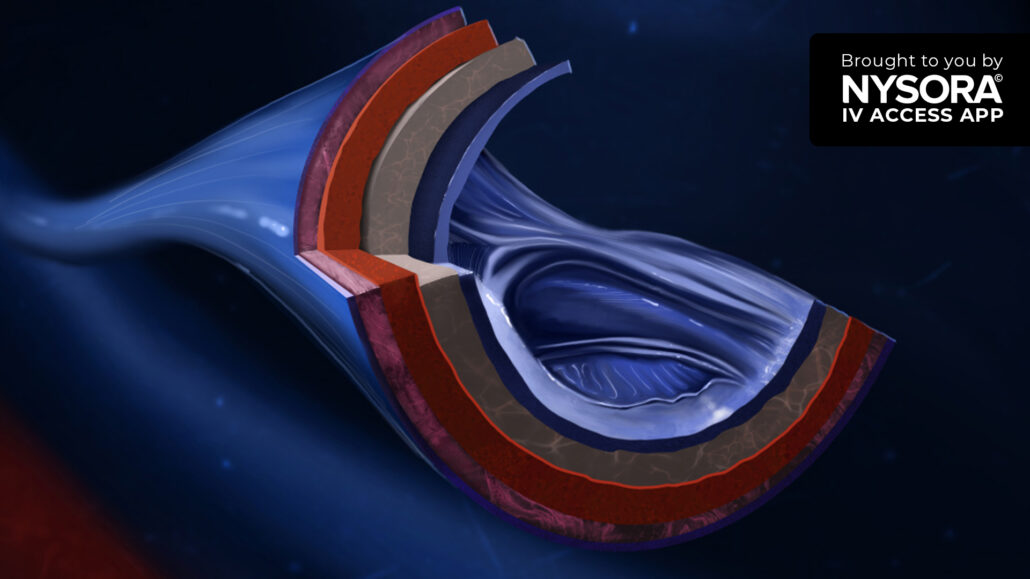
To ensure safe IV access, it’s vital to distinguish between veins and arteries. This knowledge is particularly important for injections and blood draws.
Here are the key differences:
- Location: Arteries are usually located deeper in the body compared to veins, which are often closer to the skin’s surface.
- Pulse: Arteries carry blood away from the heart, so they have a pulse that can often be felt. Veins do not have a palpable pulse.
- Oxygenation of blood: Typically, arteries carry oxygenated blood (except for the pulmonary artery), which is bright red in color, whereas veins carry deoxygenated blood, which is darker.
- Wall thickness and elasticity: Arteries have thicker and more elastic walls than veins, as they need to withstand higher pressure from the heart pumping blood.
- Valves: Veins often have valves that help keep blood flowing toward the heart, while arteries do not have valves (except for the aortic and pulmonary valves at their origins).
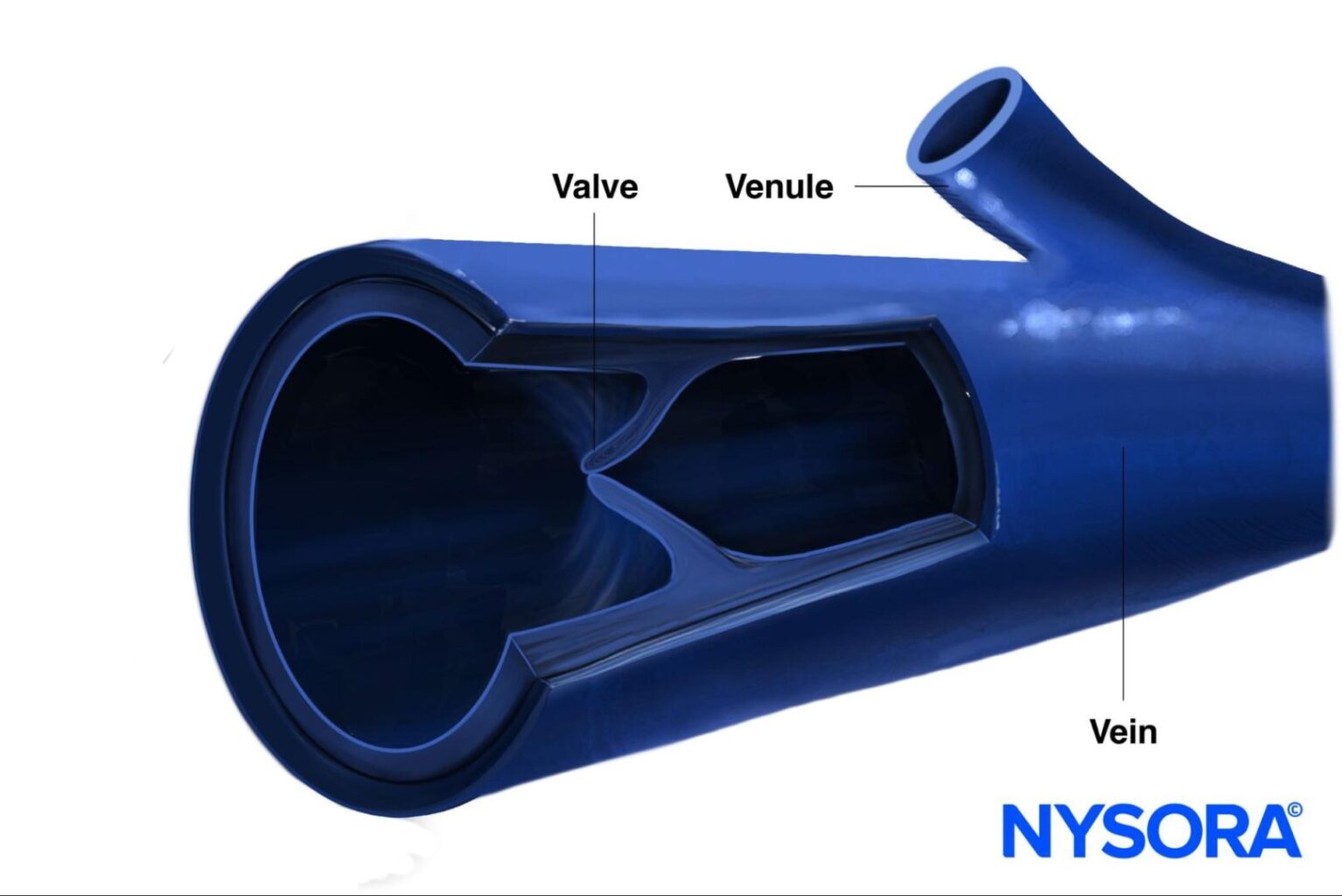
Structure of a valve in a vein.
- Pressure: Blood pressure in arteries is much higher than in veins.
- Blood flow: Blood in the arteries flows rapidly and under high pressure, while in the veins, it flows more slowly and under low pressure.
- Direction of blood flow: Arteries carry blood away from the heart, while veins carry blood back to the heart.
Advance your IV skills with the NYSORA IV Access App! Explore many resources, including easy-to-follow algorithms, expert tips, and clinical videos. Perfect for healthcare professionals at any level, download today and start improving your IV catheterization techniques!




