Tips for a Proximal Sciatic Nerve Block: Subgluteal Approach
The sciatic nerve, originating from the sacral plexus (L4-S3), provides most of the motor and sensory innervation to the leg. A proximal sciatic nerve block is indicated for anesthesia and analgesia for foot and ankle surgery, procedures on and below the knee involving the posterior aspect of the knee, and above-knee amputation.
Follow these 3 steps for a proximal sciatic nerve block using the subgluteal approach
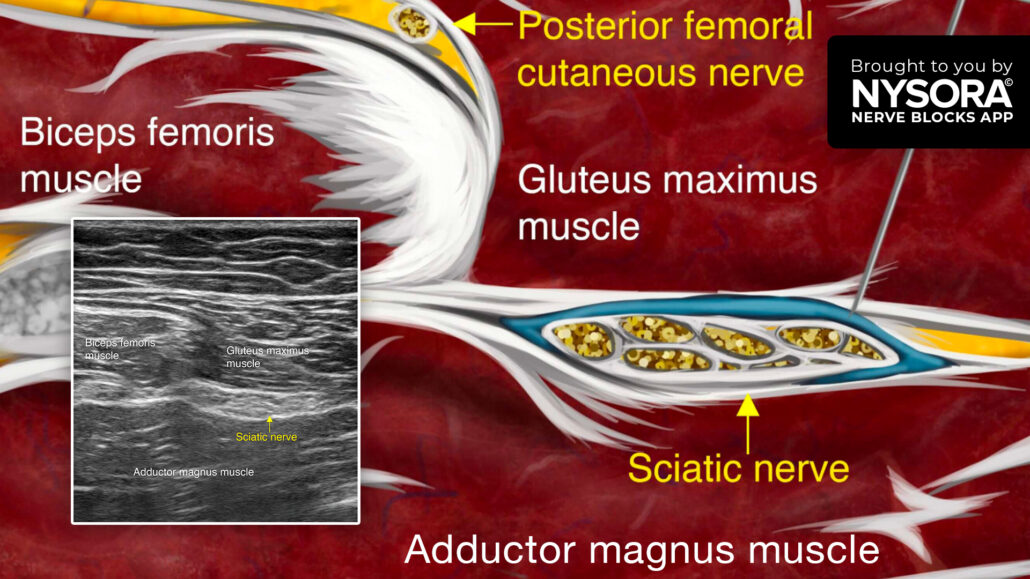
- Place the transducer over the gluteal crease to identify the fascial planes between the gluteus maximus, biceps femoris, and adductor magnus muscles.
- Identify the sciatic nerve as a hyperechoic oval structure within this fascial plane.
- Insert the needle in-plane, from lateral to medial, toward the lateral edge of the sciatic nerve within the fascial plane, and inject 10-20 mL of local anesthetic.
Watch the video below to get a better picture of the process and see how the NYSORA Nerve Blocks App brings these instructions to life:
For more tips like these and the complete guide to the 60 most frequently used nerve blocks, download the Nerve Blocks App HERE. Don’t miss the chance to get the bestselling NYSORA Nerve Blocks App in book format – the perfect study companion with the Nerve Blocks app!