Ultrasound Pain Block Tip of the Week: Suprascapular Nerve Block
Shoulder pain can severely affect the quality of life in people with indications such as adhesive capsulitis, frozen shoulder, rotator cuff tear, and glenohumeral arthritis secondary to degeneration or inflammation.
A suprascapular nerve block is is a safe and effective method used for the management of acute and chronic shoulder pain. Today, we are sharing 3 tips to successfully perform a suprascapular nerve block:
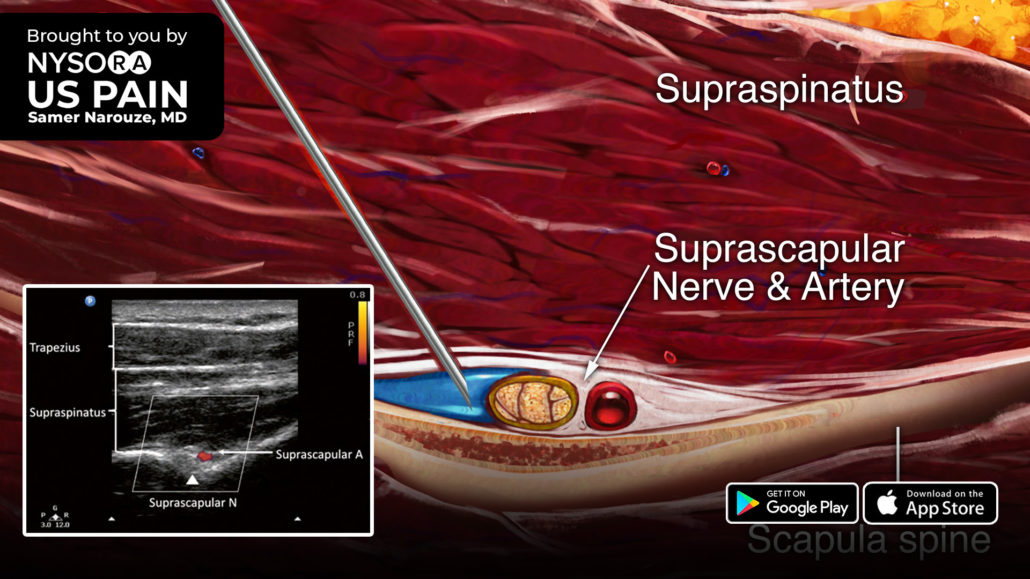
- Position the transducer in a coronal plane over the suprascapular fossa with a slight anterior tilt.
- Identify the suprascapular nerve on the floor of the scapular spine between the suprascapular notch and spinoglenoid notch. The suprascapular nerve and artery run underneath the fascia of the supraspinatus muscle.
- Insert the needle in-plane from the medial side of the transducer and inject 5-8 mL of local anesthetic.
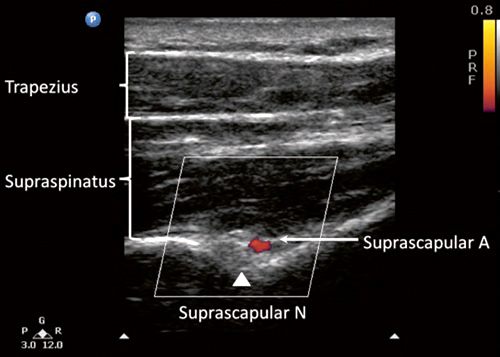
Sonoanatomy
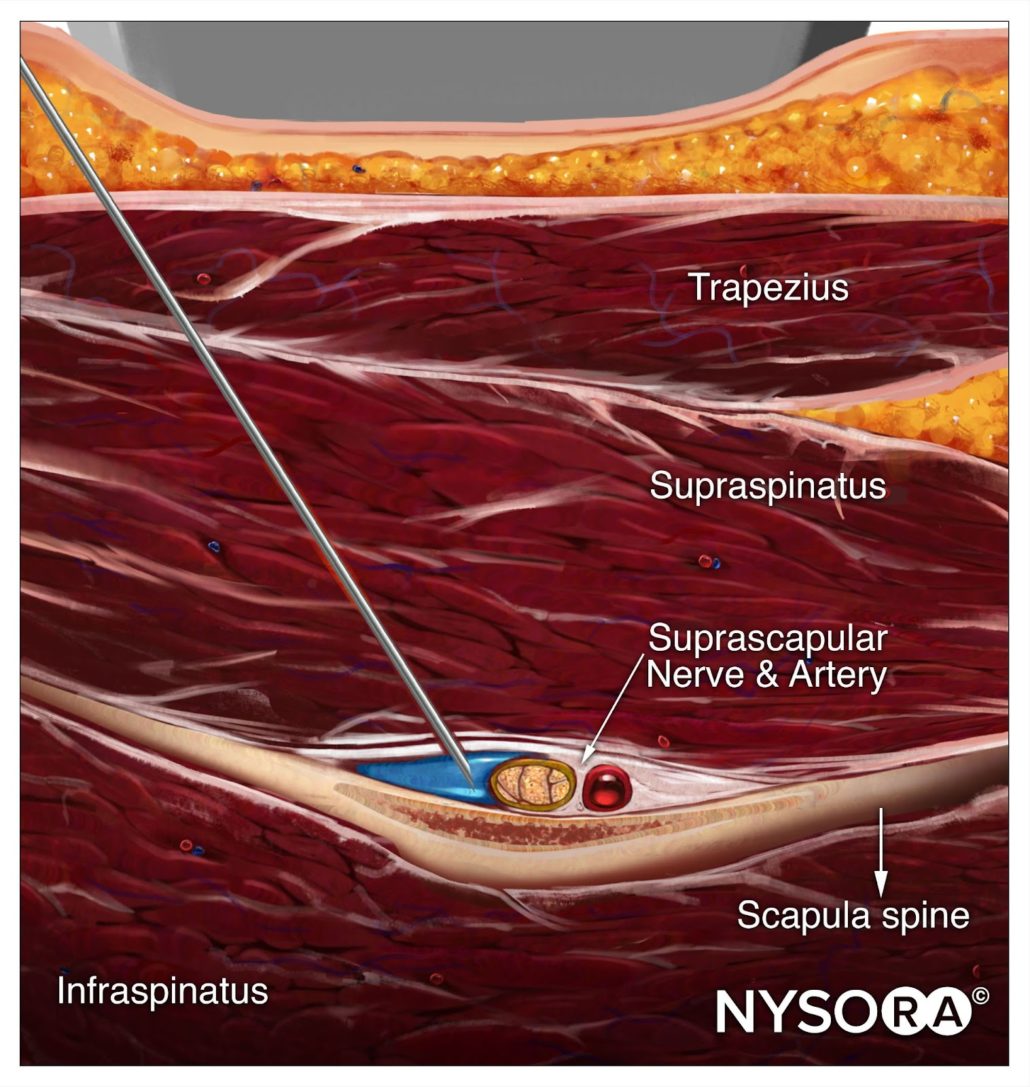
Reverse Ultrasound Anatomy
Comparison of sonoanatomy and reverse ultrasound anatomy for a suprascapular nerve block.
Check out the all-new reverse ultrasound anatomy illustration and slider image in the Ultrasound Pain App by Samer Narouze. Head over to the “Suprascapular Nerve Block > Technique” section for a complete understanding of the principles of the technique.
Download the US Pain App HERE to read other tips on managing acute and chronic pain and to access the complete guide to ultrasound-guided chronic pain blocks.



